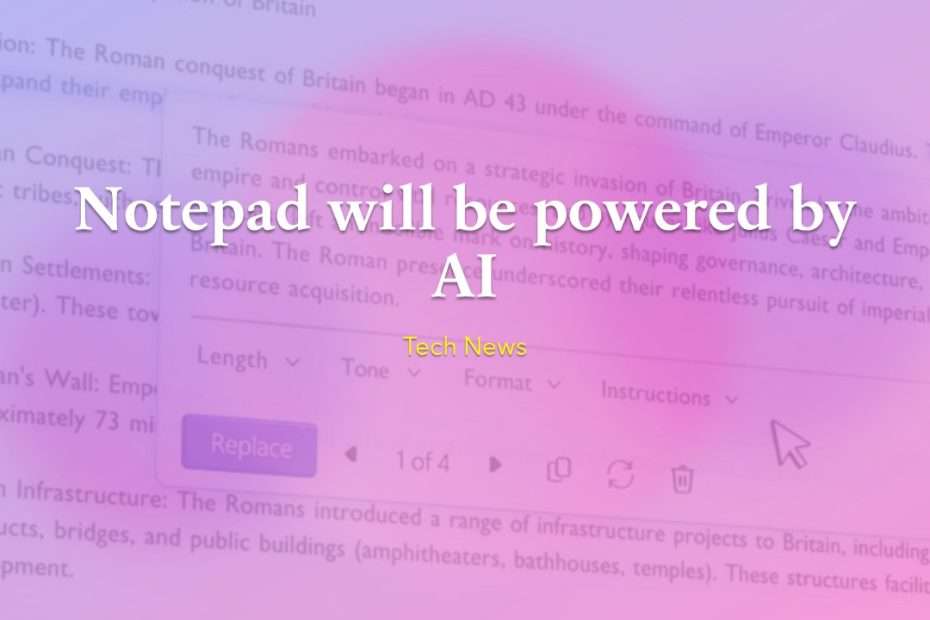
In the ever-expanding landscape of technological integration, companies continue to incorporate AI into a wide array of products and services. A notable example of this trend is Microsoft’s forthcoming update, codenamed Hudson Valley, which introduces a generative AI feature to the unassuming Notepad app. This development showcases the pervasive nature of artificial intelligence, transcending traditional boundaries and finding applications even in seemingly straightforward tools like text editors.
Twitter user @PhantomOcean3, also known as X, recently shared a screenshot unveiling the Notepad AI feature called Cowriter. This innovative addition operates similarly to other generative AI tools by utilizing artificial intelligence to manipulate text. Specifically, Cowriter can rewrite content, adjusting its length, tone, or format based on user preferences. The introduction of such AI capabilities into a simple and commonly used application like Notepad demonstrates the ongoing integration of advanced technologies into everyday tools, offering users a more dynamic and personalized experience when working with text.
New Notepad feature soon™️ pic.twitter.com/yv6axwuG2e
— PhantomOcean3 ☃️ (@PhantomOfEarth) January 9, 2024
The revealed screenshot suggests that Cowriter, the new Notepad AI feature, will implement a credits system similar to the one utilized in Paint’s DALL-E 3-powered Cocreator feature. This system functions by assigning a specific number of credits, which decrease with each use of the AI. However, Microsoft has not disclosed crucial details about this credit system, such as the initial allocation of credits for users, the frequency of their restoration, or the pricing structure for purchasing additional credits. The adoption of this credit-based approach adds an interesting dimension to the implementation of AI in everyday applications, raising questions about accessibility, usage limits, and the potential economic considerations for users.
As the details surrounding Cowriter’s credits system remain undisclosed, users are left with uncertainties regarding the practical aspects of utilizing this AI feature. Microsoft’s decision to incorporate a credit-based model into Cowriter, without providing clarity on key parameters, introduces a level of intrigue and speculation. The opacity surrounding credit allocation, restoration frequency, and cost invites further exploration into the intricacies of integrating AI functionalities within widely used applications, highlighting the evolving nature of AI-based interactions and their impact on user engagement.
In the latest test build of Windows 11, references to Cowriter have emerged within the program files, indicating Microsoft’s ongoing development and integration of this new AI feature into the Notepad application. The inclusion of a waitlist for Cowriter and the presence of a hero image designed for potential marketing efforts further suggest that Microsoft is gearing up for an official announcement. The proactive steps taken, such as preparing promotional materials and establishing a waitlist, hint at the company’s intention to generate anticipation and interest surrounding the introduction of Cowriter to the user base. This discovery underscores the dynamic nature of software development, with companies strategically building excitement around upcoming features through subtle hints and preparatory measures.

The identification of references to Cowriter, a waitlist, and marketing assets within the Windows 11 test build unveils Microsoft’s deliberate preparations for the formal unveiling of this AI-powered Notepad feature. The findings provide a glimpse into the meticulous planning and promotional strategies employed by tech companies as they introduce new functionalities. Microsoft’s approach in laying the groundwork for the Cowriter release exemplifies the industry’s focus not only on technological innovation but also on creating a buzz and engaging user interest in anticipation of product launches.
In recent years, the longstanding Notepad app has undergone significant updates to enhance its functionality and user experience. Notable improvements introduced by Microsoft in 2021 encompassed the addition of a dark mode, Mica visuals, enhanced find/replace capabilities, and multi-level undo tools. Subsequent updates continued to elevate the utility of Notepad, incorporating features like browser-style tabs, character counts, and an autosave function. These advancements reflect Microsoft’s commitment to refining the user interface and capabilities of a seemingly basic application, underscoring the company’s recognition of the enduring importance of Notepad in its suite of tools.
The decision to discontinue WordPad, a software that has been in existence for 30 years, offers insights into Microsoft’s strategic shift and renewed focus on improving Notepad. With ongoing enhancements and the retirement of WordPad, it becomes evident that Microsoft is actively streamlining its suite of applications, prioritizing the development and refinement of specific tools to meet the evolving needs of users. The evolution of Notepad, from its traditional simplicity to a more feature-rich application, aligns with Microsoft’s broader strategy of adapting and modernizing its software offerings to align with contemporary usage patterns and user expectations.
Anticipated as the potential Windows 12, the Hudson Valley update is poised to introduce a comprehensive integration of AI features throughout the operating system. This ambitious endeavor signifies a significant step forward in Microsoft’s commitment to infuse artificial intelligence into various aspects of the user experience. The incorporation of AI is expected to extend across nearly every element of the OS, showcasing a holistic approach to leveraging advanced technologies for enhanced functionality. Additionally, the update aims to address practical concerns such as storage space, boasting a modular design that is anticipated to occupy less storage. The promise of faster updates and heightened security further highlights Microsoft’s dedication to refining the overall performance and user satisfaction within the Windows ecosystem.
Microsoft stands out as a trailblazer in fully embracing artificial intelligence (AI), having invested a substantial sum of approximately $13 billion in its collaboration with OpenAI. This formidable partnership underscores Microsoft’s commitment to integrating AI technologies into its products and services. A recent development in this trajectory is the introduction of a dedicated Copilot key on new Windows keyboards. This significant alteration marks a departure from the standard Windows keyboard layout, which has remained relatively unchanged since the inception of the Windows key in 1994. The addition of the Copilot key exemplifies Microsoft’s dedication to pushing the boundaries of conventional user interfaces, bringing AI capabilities to the forefront of user interactions.
The integration of generative AI into the humble Notepad app reflects a broader industry shift towards incorporating advanced technologies into everyday tools. Microsoft’s decision to enhance a basic text editor with AI capabilities underlines the versatility of these technologies, as they become increasingly prevalent in various aspects of our digital lives. The constant evolution and integration of AI across diverse platforms highlight the ongoing effort to leverage advanced capabilities, even in the most unexpected corners of our daily technology usage.
Maybe you liked other interesting articles?